Computer Networks - (LAB PROGRAMS)
Aim:
☛ Implement Dijsktra’s algorithm to compute the shortest path through a network
Solution :
Dijsktra's algorithm to compute the shortest path
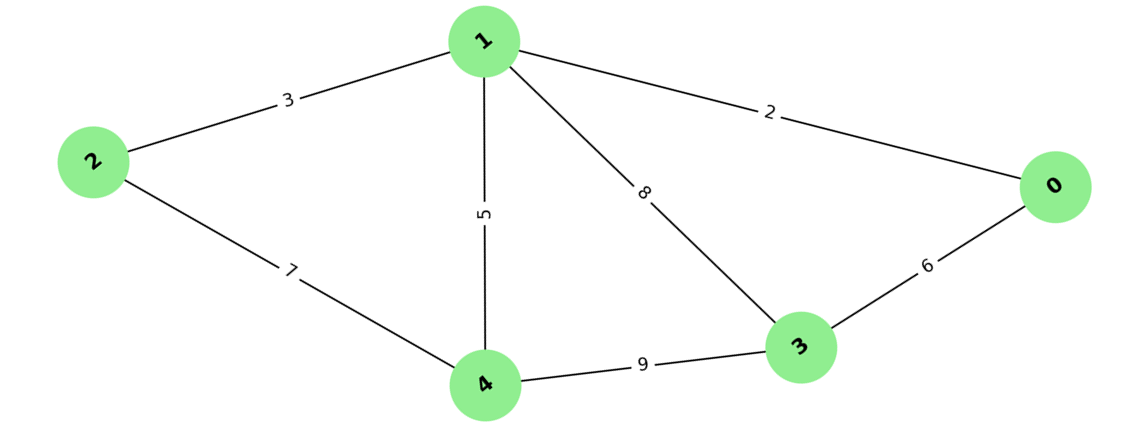
Input Graph:
Source Code:
File Name: dijsktras.c
#include<stdio.h>
#define INFINITY 9999
#define MAX 10
// Function declaration
void dijkstra(int graph[MAX][MAX], int numVertices, int startNode);
int main() {
int graph[MAX][MAX], numVertices, i, j, startNode;
// Input number of vertices
printf("Enter the number of vertices: ");
scanf("%d", &numVertices);
// Input adjacency matrix
printf("\nEnter the adjacency matrix:\n");
for (i = 0; i < numVertices; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < numVertices; j++) {
scanf("%d", &graph[i][j]);
}
}
// Input the starting node
printf("\nEnter the starting node (0 to %d): ", numVertices - 1);
scanf("%d", &startNode);
// Run Dijkstra's algorithm
dijkstra(graph, numVertices, startNode);
return 0;
}
// Dijkstra's algorithm implementation
void dijkstra(int graph[MAX][MAX], int numVertices, int startNode) {
int cost[MAX][MAX];
int distance[MAX]; // Shortest distances from startNode
int predecessor[MAX]; // To store the shortest path tree
int visited[MAX]; // To mark visited nodes
int count, minDistance, nextNode, i, j;
// Create cost matrix (replace 0 with INFINITY, except on diagonal)
for (i = 0; i < numVertices; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < numVertices; j++) {
if (graph[i][j] == 0 && i != j)
cost[i][j] = INFINITY;
else
cost[i][j] = graph[i][j];
}
}
// Initialize distances, predecessors, and visited array
for (i = 0; i < numVertices; i++) {
distance[i] = cost[startNode][i];
predecessor[i] = startNode;
visited[i] = 0;
}
distance[startNode] = 0;
visited[startNode] = 1;
count = 1;
// Find shortest path for all vertices
while (count < numVertices - 1) {
minDistance = INFINITY;
// Find the next node with the smallest tentative distance
for (i = 0; i < numVertices; i++) {
if (!visited[i] && distance[i] < minDistance) {
minDistance = distance[i];
nextNode = i;
}
}
visited[nextNode] = 1;
// Update distances of neighboring unvisited nodes
for (i = 0; i < numVertices; i++) {
if (!visited[i] && (minDistance + cost[nextNode][i] < distance[i])) {
distance[i] = minDistance + cost[nextNode][i];
predecessor[i] = nextNode;
}
}
count++;
}
// Print the shortest distance and path from startNode to each other node
for (i = 0; i < numVertices; i++) {
if (i != startNode) {
printf("\nDistance from node %d to node %d = %d", startNode, i, distance[i]);
printf("\nPath: %d", i);
j = i;
while (j != startNode) {
j = predecessor[j];
printf(" <- %d", j);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
}
Output:
$ gcc dijsktras.c
$ ./a.out
Enter the number of vertices: 5
Enter the adjacency matrix:
0 2 0 6 0
2 0 3 8 5
0 3 0 0 7
6 8 0 0 9
0 5 7 9 0
Enter the starting node (0 to 4): 0
Distance from node 0 to node 1 = 2
Path: 1 <- 0
Distance from node 0 to node 2 = 5
Path: 2 <- 1 <- 0
Distance from node 0 to node 3 = 6
Path: 3 <- 0
Distance from node 0 to node 4 = 7
Path: 4 <- 1 <- 0
Related Content :
Computer Networks Lab Programs
1) Implement the data link layer framing methods such as character, character-stuffing and bit stuffing. View Solution
2) Write a program to compute CRC code for the polynomials CRC-12, CRC-16 and CRC CCIP View Solution
3) Develop a simple data link layer that performs the flow control using the sliding window protocol, and loss recovery using the Go-Back-N mechanism. View Solution
4) Implement Dijsktra’s algorithm to compute the shortest path through a network View Solution
5) Take an example subnet of hosts and obtain a broadcast tree for the subnet. View Solution
6) Implement distance vector routing algorithm for obtaining routing tables at each node. View Solution
7) Implement data encryption and data decryption View Solution
8) Write a program for congestion control using Leaky bucket algorithm. View Solution
9) Write a program for frame sorting techniques used in buffers. View Solution
10) Wireshark
i. Packet Capture Using Wire shark
ii. Starting Wire shark
iii. Viewing Captured Traffic
iv.Analysis and Statistics & Filters. View Solution
11) How to run Nmap scan View Solution
12) Operating System Detection using Nmap View Solution
13) Do the following using NS2 Simulator
i. NS2 Simulator-Introduction
ii. Simulate to Find the Number of Packets Dropped
iii. Simulate to Find the Number of Packets Dropped by TCP/UDP
iv. Simulate to Find the Number of Packets Dropped due to Congestion
v. Simulate to Compare Data Rate & Throughput.
vi. Simulate to Plot Congestion for Different Source/Destination
vii. Simulate to Determine the Performance with respect to Transmission of Packets View Solution