Creating and Running
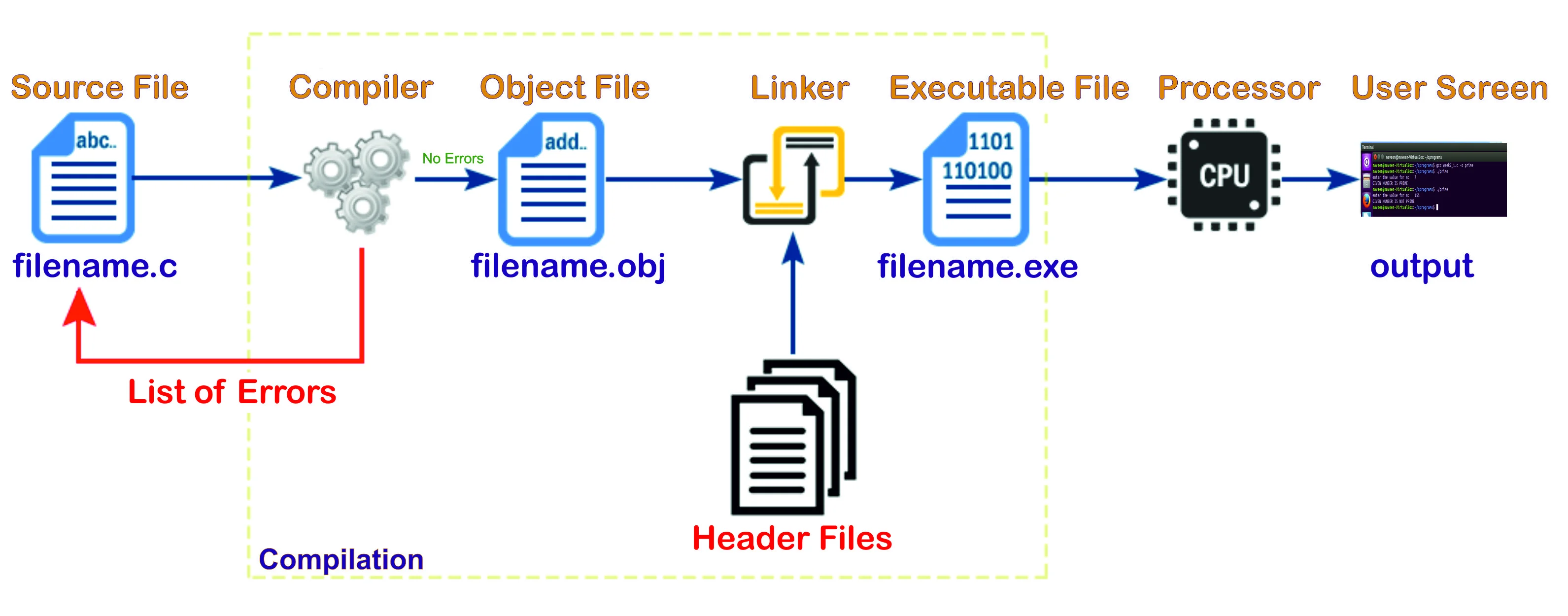
Program consists of set of instructions written in a High-level language like English. The computer only understands Low-level language. We need a translator to convert high-level language to low-level language and vice versa. We have two translators known as compiler and interpreter.
Many of the popular programming languages use the compiler as a translator. The job of compile is to translate the set of instructions to low-level language, while translating it checks the syntax of the instruction if any error (Wrong syntax) it will list all the errors.
There are 4 steps Creating and Running a Program
- Writing and Editing
- Compiling
- Linkers
- Executing
Writing and Editing
To write and edit a program we use Text editors. First we open the text editor and write program(set of instructions) and save the file to disk. The file is known as source file. Every c program, source file is saved with extension of '.C' example "filename.c"
The following steps are used to create a source code
- command to open editor "gedit filename.c"
- Type the program
- save the file and exit
Compiling
“Compiler” is a software that translates the source code written in a high-level language into the corresponding object code of the low-level language. Once the compilation is successfull (with out any errors) then system will generate an object file(.obj). Command for compiling the file is 'gcc filename.c'.
Linkers
Many of the high-level languages allow splitting the complex program into multiple modules. The Linker arranges the object code of all the modules that have been generated and combines with specified header file code that generates an Executable(.exe) file.
Executing
Once the executable file is created, we have to execute the program. Command for executing the file is './a.out'. The command submits the executable file to CPU; the processor performs the task specified in the source file and generates results.
Next Topic :Program Development steps