Algorithms and Flow Chart
Algorithm
DefinitionA sequence of activities to be processed for getting desired output from a given input.
Algorithm refers to a set of rules/instructions that step-by-step define how a work is to be executed upon in order to get the expected results. The Algorithm are language-independent, i.e. they are written in English like sentences that can be implemented in any language, and yet the output will be the same
Properties of algorithm
1) Finiteness: An algorithm must always terminate after a finite number of steps. It means after every step one reach closer to solution of the problem and after a finite number of steps algorithm reaches to an end point.
2) Definiteness: Each step of an algorithm must be precisely defined. It is done by well thought actions to be performed at each step of the algorithm. Also the actions are defined unambiguously for each activity in the algorithm.
3) Input: Any operation you perform need some beginning value/quantities associated with different activities in the operation. So the value/quantities are given to the algorithm before it begins.
4) Output: One always expects output/result (expected value/quantities) in terms of output from an algorithm. The result may be obtained at different stages of the algorithm. If some result is from the intermediate stage of the operation then it is known as intermediate result and result obtained at the end of algorithm is known as end result. The output is expected value/quantities always have a specified relation to the inputs.
5) Effectiveness: Algorithms to be developed/written using basic operations. Actually operations should be basic, so that even they can in principle be done exactly and in a finite amount of time by a person, by using paper and pencil only.
Advantages
- Easy to write.
- Human readable techniques to understand the logic.
- Algorithms for big problems can be written with moderate efforts.
Disadvantages
- Difficult to debug.
- Difficult to show branching and looping.
- Jumping (goto) makes it hard to trace some problems.
flowchart
DefinitionA flowchart is a pictorial or graphical representation of a process
Flowcharts normally use standard symbols to represent the different types of instructions. These symbols are used to construct the flowchart and show the step-by-step solution to the problem. The flow chart symbols are linked together with arrows showing the process flow direction. This pictorial representation can give a step-by-step solution to the given problem.
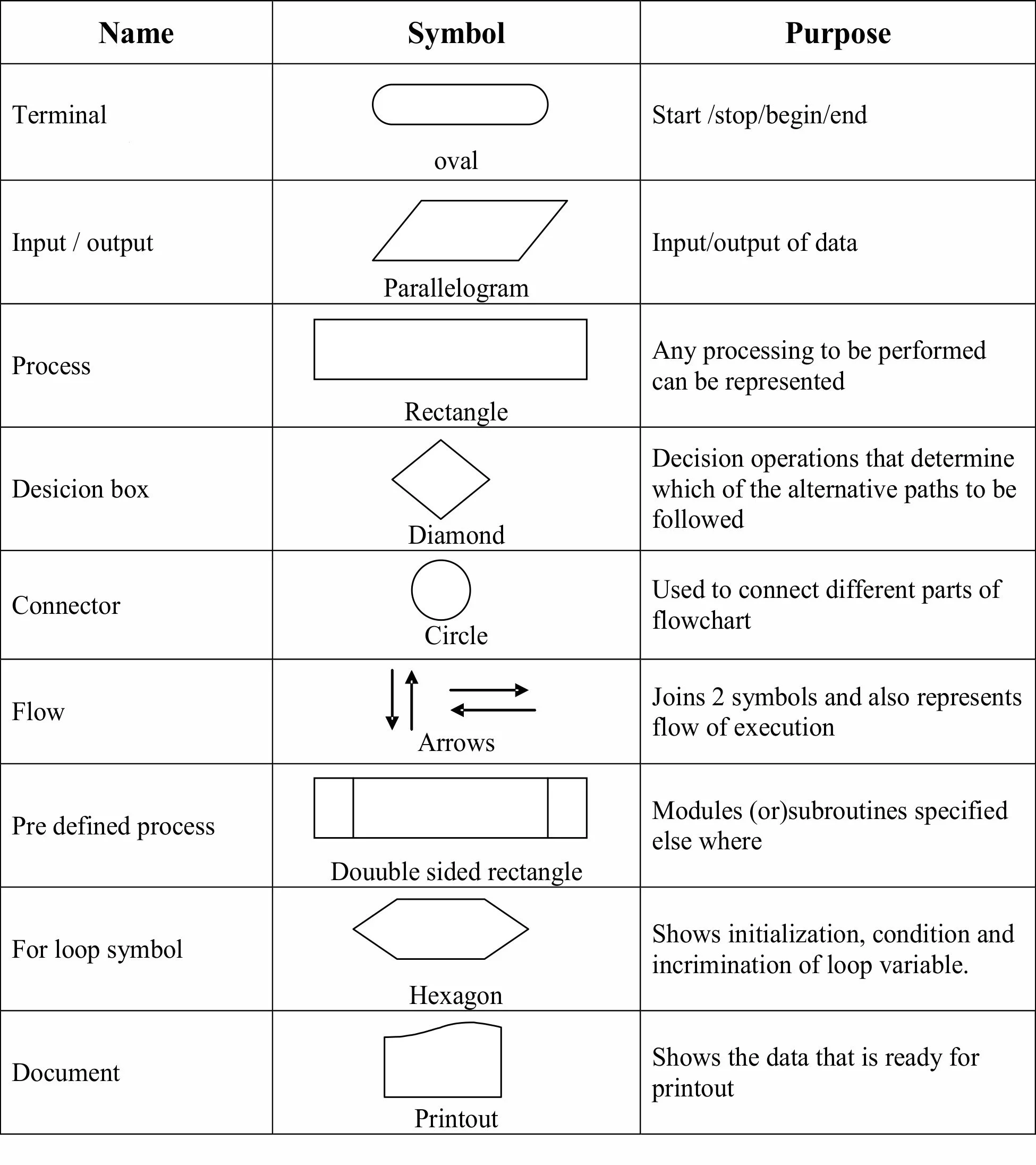
General Rules for flowcharting
1. All boxes of the flowchart are connected with Arrows. (Not lines)
2. Flowchart symbols have an entry point on the top of the symbol with no other entry points. The exit point for all flowchart symbols is on the bottom except for the Decision symbol.
3. The Decision symbol has two exit points; these can be on the sides or the bottom and one side.
4. Generally a flowchart will flow from top to bottom. However, an upward flow can be shown as long as it does not exceed 3 symbols.
5. Connectors are used to connect breaks in the flowchart. Examples are
- From one page to another page.
- An upward flow of more then 3 symbols
6. Subroutines and Interrupt programs have their own and independent flowcharts.
7. All flow charts start with a Terminal or Predefined Process (for interrupt programs or subroutines) symbol.
8. All flowcharts end with a terminal or a contentious loop.
Advantages
- Easy to draw.
- Easy to understand the logic.
- Easy to identify mistakes by the non-computer person.
- Easy to show branching and looping.
Disadvantages
- Time-consuming.
- Difficult to modify.
- Very difficult to draw a flowchart for big or complex problems.
| Block by block information diagram representing the data flow. | Step by step instruction representing the process of any solution. |
| It is a pictorial representation of a process. | It is a stepwise analysis of the work to be done. |
| The solution is shown in a graphical format. | The solution is shown in a non-computer language like English. |
| Easy to understand as compared to the algorithm. | It is somewhat difficult to understand. |
| Easy to show branching and looping. | Difficult to show branching and looping. |
| Flowchart for a big problem is impractical. | The algorithm can be written for any problem. |
| Difficult to debug errors. | Easy to debug errors. |
| It is easy to make a flowchart. | It is difficult to write an algorithm as compared to a flowchart. |
Next Topic :Introduction to C