Levels of Abstraction in DBMS
Data Abstraction is a process of hiding unwanted or irrelevant details from the end user. It provides a different view and helps in achieving data independence which is used to enhance the security of data.
The database systems consist of complicated data structures and relations. For users to access the data easily, these complications are kept hidden, and only the relevant part of the database is made accessible to the users through data abstraction.
Levels of abstraction for DBMS
Database systems include complex data-structures. In terms of retrieval of data, reduce complexity in terms of usability of users and in order to make the system efficient, developers use levels of abstraction that hide irrelevant details from the users. Levels of abstraction simplify database design.
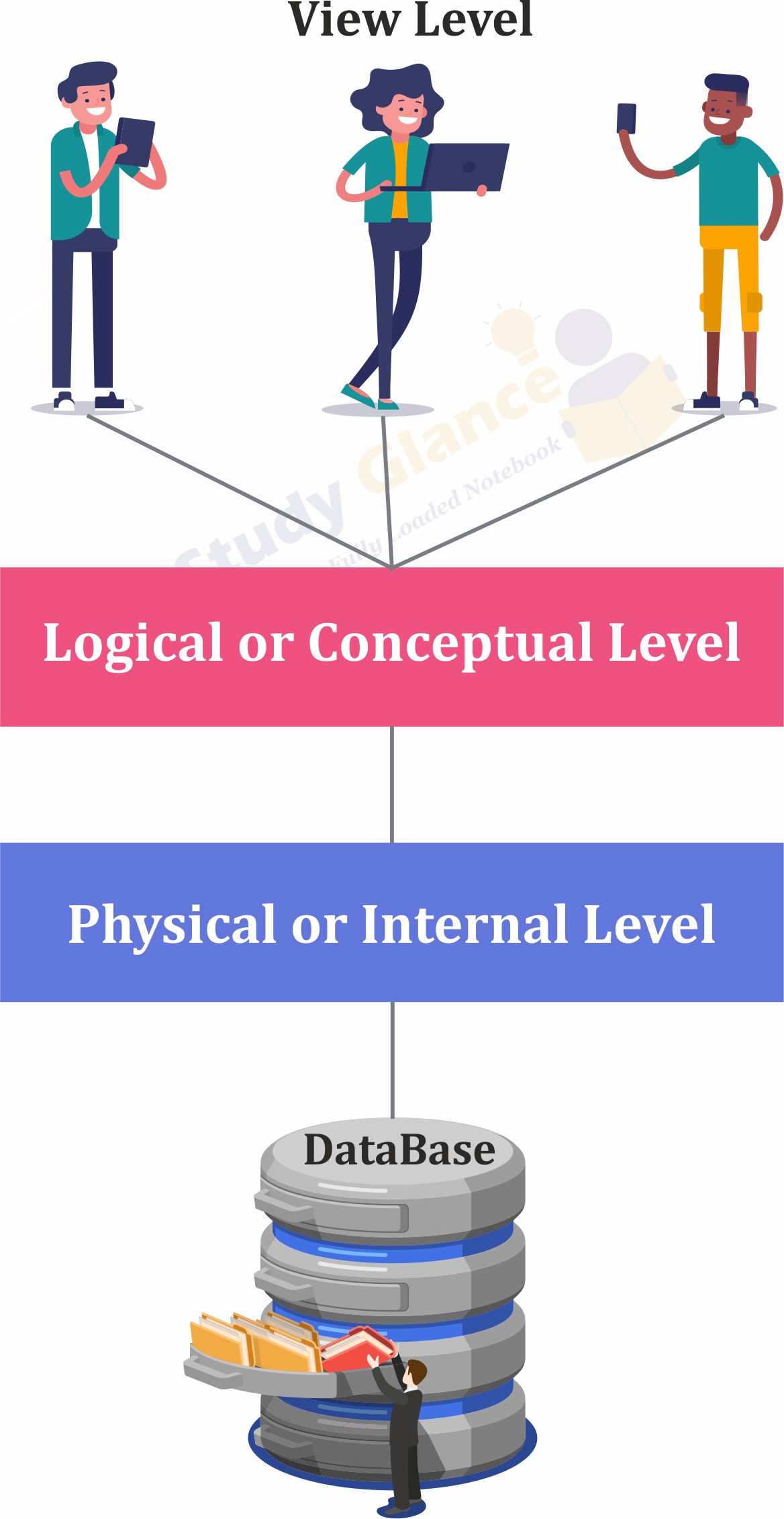
Mainly there are three levels of abstraction for DBMS
- Physical or Internal Level
- Logical or Conceptual Level
- View or External Level
1. Physical or Internal Level
The internal level has an internal schema which describes the physical storage structure of the database.
The internal schema is also known as a physical schema.
It uses the physical data model. It is used to define that how the data will be stored in a block.
The physical level is used to describe complex low-level data structures in detail.
Facts about Internal schema
- The internal schema is the lowest level of data abstraction
- It helps you to keeps information about the actual representation of the entire database. Like the actual storage of the data on the disk in the form of records
- The internal view tells us what data is stored in the database and how
2. Logical or Conceptual Level
The conceptual schema describes the design of a database at the conceptual level. Conceptual level is also known as logical level.
The conceptual schema describes the structure of the whole database.
The conceptual level describes what data are to be stored in the database and also describes what relationship exists among those data.
In the conceptual level, internal details such as an implementation of the data structure are hidden.
Programmers and database administrators work at this level.
Facts about Conceptual schema
- Defines all database entities, their attributes, and their relationships
- Security and integrity information
- In the conceptual level, the data available to a user must be contained in or derivable from the physical level.
3. View or External Level
It hides the unrelated details of the database from the user. There may be “n” number of external views for each database.
Each external view is defined using an external schema, which consists of definitions of various types of external record of that specific view.
View level can be used by all users (all levels' users). This level is the least complex and easy to understand.
Facts about External schema
- An external level is only related to the data which is viewed by specific end users.
- This level includes some external schemas.
- External schema level is nearest to the user
- An external schema is also known as view schema.
- Each view schema describes the database part that a particular user group is interested and hides the remaining database from that user group.
- The view schema describes the end user interaction with database systems.
Next Topic :Structure of DBMS