Introduction
What is Data
Data can be defined as a representation of facts, concepts, or instructions in a formalized manner, which should be suitable for communication, interpretation, or processing by human or electronic machine.
In other words, The Data is collection of objects defined by attributes.
A data object represents an entity.
- Also called as record, sample, example, instance, data point, object, tuple.
Examples:
- In a sales database, the objects may be customers, store items, and sales;
- In a medical database, the objects may be patients;
- In a university database, the objects may be students, professors, and courses.
Data objects are described by attributes, in other words, A collection of attributes describes an object.
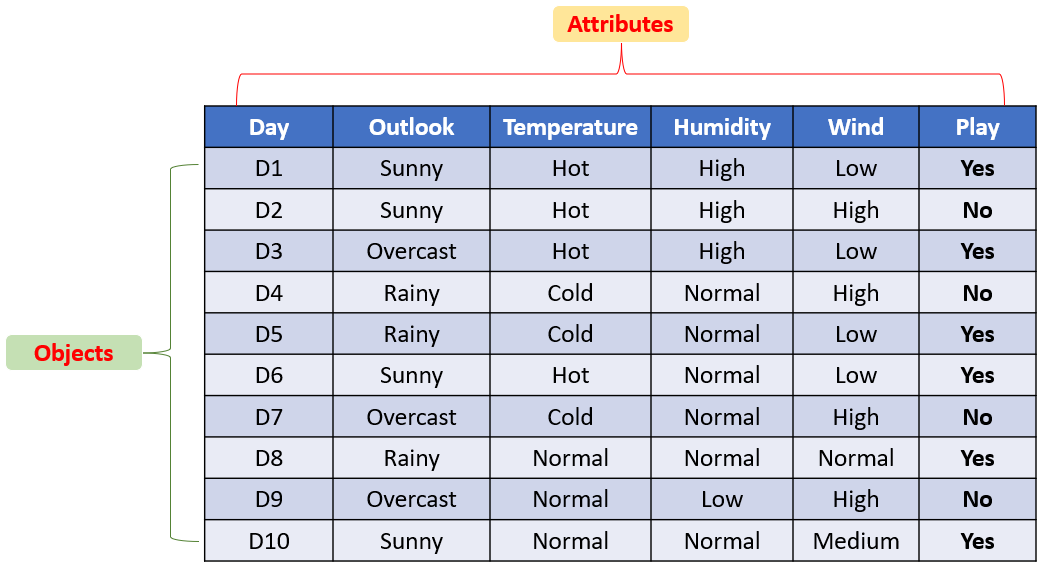
database rows → data objects
database columns → attributes
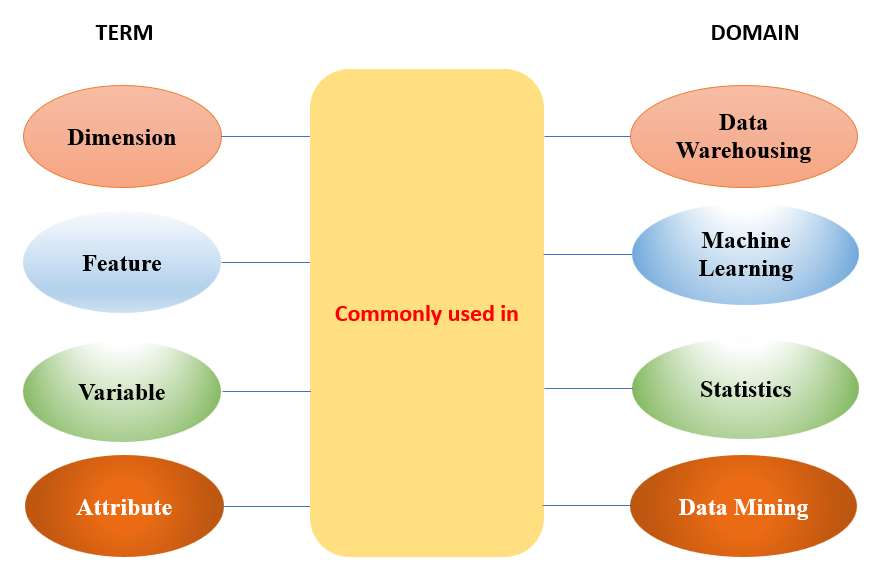
Attributes
An attribute is a data field, representing property or feature of a data object.
- Also known as dimension, feature, and variable.
Examples:
weight of a person, height, temperature, customer _ID, name, address etc.
What is Data Mining
DefinitionData mining is the process of discovering interesting patterns and knowledge from large amounts of data. The data sources can include databases, data warehouses, the Web, other information repositories, or data that are streamed into the system dynamically.
(or)Definition
Data Mining is a process of finding potentially useful patterns and valuable information from huge amount of data.
(or)Definition
Data Mining is all about discovering hidden, unsuspected, and previously unknown yet valid relationships amongst the data.
(or)Definition
Transforming tremendous amounts of data into organized knowledge.
(or)Definition
Data Mining is also called as Knowledge discovery, Knowledge extraction, data/pattern analysis, Information extraction, data dredging, etc.
Data Mining Applications
- Insurance: Data mining helps insurance companies to price their products profitable and deciding whether to approve policy applications, including risk modelling and management for prospective customers.
- Education: Data mining benefits educators to access student data, predict achievement levels and find students or groups of students which need extra attention. For example, students who are weak in maths subject.
- Banking: Data mining helps finance sector to get a view of market risks and manage regulatory compliance. It helps banks to identify probable defaulters to decide whether to issue credit cards, loans, etc. Bank and credit card companies use data mining tools to build financial risk models, detect fraudulent transactions and examine loan and credit applications.
- Retail: Data Mining techniques help retail malls and grocery stores identify and arrange most sellable items in the most attentive positions. It helps store owners to comes up with the offer which encourages customers to increase their spending. Online retailers mine customer data and internet clickstream records to help them target marketing campaigns, ads and promotional offers to individual shoppers.
- Service Providers: Service providers like mobile phone and utility industries use Data Mining to predict the reasons when a customer leaves their company. They analyse billing details, customer service interactions, complaints made to the company to assign each customer a probability score and offers incentives.
- E-Commerce: E-commerce websites use Data Mining to offer cross-sells and up-sells through their websites. One of the most famous names is Amazon, who use Data mining techniques to get more customers into their eCommerce store.
- Super Markets: Data Mining allows supermarket’s develop rules to predict if their shoppers were likely to be expecting. By evaluating their buying pattern, they could find woman customers who are most likely pregnant. They can start targeting products like baby powder, baby shop, diapers and so on.
- Entertainment: Streaming services do data mining to analyse what users are watching or listening to and to make personalized recommendations based on people's viewing and listening habits.
- Healthcare: Data mining helps doctors diagnose medical conditions, treat patients and analyse X-rays and other medical imaging results. Medical research also depends heavily on data mining, machine learning and other forms of analytics.
Next Topic :Attribute Types