Quick Sort
Quick Sort was invented by Charles Antony Richard Hoare (Tony Hoare or C. A. R. Hoare) in the year 1959. His paper, "Quicksort", published in 1961, introduced the algorithm and its key properties, highlighting its efficient sorting capabilities.
Quick Sort is a highly efficient sorting algorithm and is based on a divide and conquer strategy. Algorithm consider a sorting method that performs very well on larger arrays and lists. At each step in the method, the goal is to place a particular (pivot) element in its final position within the array. In so doing, "all elements to the left of pivot are smaller than the pivot and all elements to the right of pivot are greater than or equal to the pivot". This technique essentially partitions the array into two sub-arrays. The same process can then be applied to each of these sub-arrays and repeated until all elements are placed in their final positions.
This quick sort method of sorting is also called partition-exchange procedure. Each time a sub-array is divided into two smaller sub-arrays; these can be processed in turn using either an iterative or recursive.
 source from miro.medium.com
source from miro.medium.com
Step by Step Process of Quick Sort
- Pivot Selection: First, select an element from the array to be the pivot. This can be the first, last, middle, or even a random element. The choice of pivot can affect the performance of the algorithm.
- Partitioning: Rearrange the array so that all elements with values less than the pivot come before the pivot, while all elements with values greater than the pivot come after it. The pivot then is in its final position. This operation is known as partitioning.
- Recursion: Apply the above steps recursively to the sub-array of elements with smaller values and separately to the sub-array of elements with greater values.
- The recursion stops when the sub-array has less than two elements.
function quickSort(arr, low, high)
if low < high then
// pi is partitioning index, arr[pi] is now at right place
pi := partition(arr, low, high)
// Separately sort elements before partition and after partition
quickSort(arr, low, pi - 1)
quickSort(arr, pi + 1, high)
function partition(arr, low, high)
// pivot (Element to be placed at right position)
pivot := arr[high]
i := (low - 1) // Index of smaller element
for j = low to high - 1 do
// If current element is smaller than the pivot
if arr[j] < pivot then
i := i + 1
swap arr[i] with arr[j]
// swap arr[i+1] and arr[high] (or pivot)
swap arr[i + 1] with arr[high]
return (i + 1)
// Utility function to swap two elements in an array
function swap(a, b)
temp = a
a = b
b = tempQuick sort Example
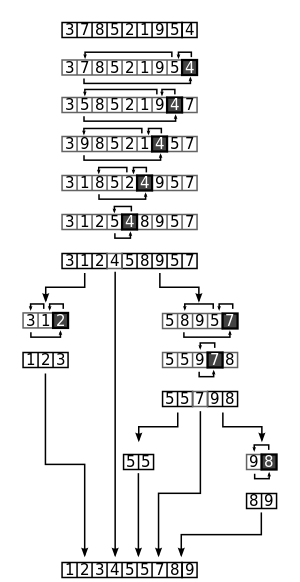 from wikipedia
from wikipediaTime complexity of the Quick Sort Algorithm
- Best-case: O(n log n) occurs when the pivot element chosen perfectly divides the array into two equal halves with elements smaller than the pivot on one side and larger elements on the other. This scenario results in balanced recursion, leading to efficient sorting.
- Average-case: O(n log n) is also the expected complexity in real-world scenarios. Choosing a random pivot element throughout the sort creates roughly balanced sub-arrays on average, maintaining efficient overall performance.
- Worst-case: O(n2) happens when the chosen pivot element is always the smallest or largest element in the sub-array. This results in one sub-array remaining almost unsorted throughout the recursion, leading to quadratic time complexity.
#include <stdio.h>
// Function to swap two elements
void swap(int* a, int* b)
{
int t = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = t;
}
int partition(int arr[], int low, int high)
{
int pivot = arr[high];
int i = (low - 1);
for (int j = low; j <= high - 1; j++)
{
if (arr[j] < pivot) {
i++;
swap(&arr[i], &arr[j]);
}
}
swap(&arr[i + 1], &arr[high]);
return (i + 1);
}
void quickSort(int arr[], int low, int high) {
if (low < high) {
int pi = partition(arr, low, high);
quickSort(arr, low, pi - 1);
quickSort(arr, pi + 1, high);
}
}
int main()
{
int list[20],size,i;
printf("Enter size of the list: ");
scanf("%d",&size);
printf("Enter %d integer values: ",size);
for(i = 0; i < size; i++)
scanf("%d",&list[i]);
quickSort(list,0,size-1);
printf("List after sorting is: ");
for(i = 0; i < size; i++)
printf(" %d",list[i]);
return 0;
}Next Topic :Merge Sort